UVA vs UVB Explained: Why You Need UV Protection Glasses Now
UVA, UVB, UV 400—are these terms confusing you? You are not alone! While buying UV protection glasses, these terms confuse a lot. It is like finding your car in a packed parking lot where all the cars look the same!
But don’t worry; we’ve got you covered! In this guide, we will clear all your doubts about UVA & UVB, UV 400, and help you choose the best UV protection glasses. So that you can stay shielded and stylish under the sun.
So, let’s break it down!
Table of Contents
- What is UV 400 Protection?
- What are UVA and UVB Rays?
- 6 Signs Your Glasses Don’t Have UV Protection
- Top Benefits of Wearing UV Protection Glasses Daily
- How to Choose the Best UV Protection Glasses For Your Eyes?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Can regular goggles protect your eyes from UV rays?
- Are polarized sunglasses the same as UV protection glasses?
- Is it OK to wear UV protection glasses all the time?
What is UV 400 Protection?
UV 400 protection—you might have come across this word while shopping for sunglasses.
Well, it means any high-quality sunglasses glasses with UV 400 lenses will block all the sunlight rays, including UVA and UVB.
This is the highest level of eye protection available. This ensures your eyes are completely shielded from harmful radiation. So, make sure you see the UV 400 protection label when you buy sunglasses.
What Are UVA and UVB Rays?
UVA and UVB are the two types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. But they have differences!
They have different effects on the skin and eyes owing to their different wavelength and penetration properties.
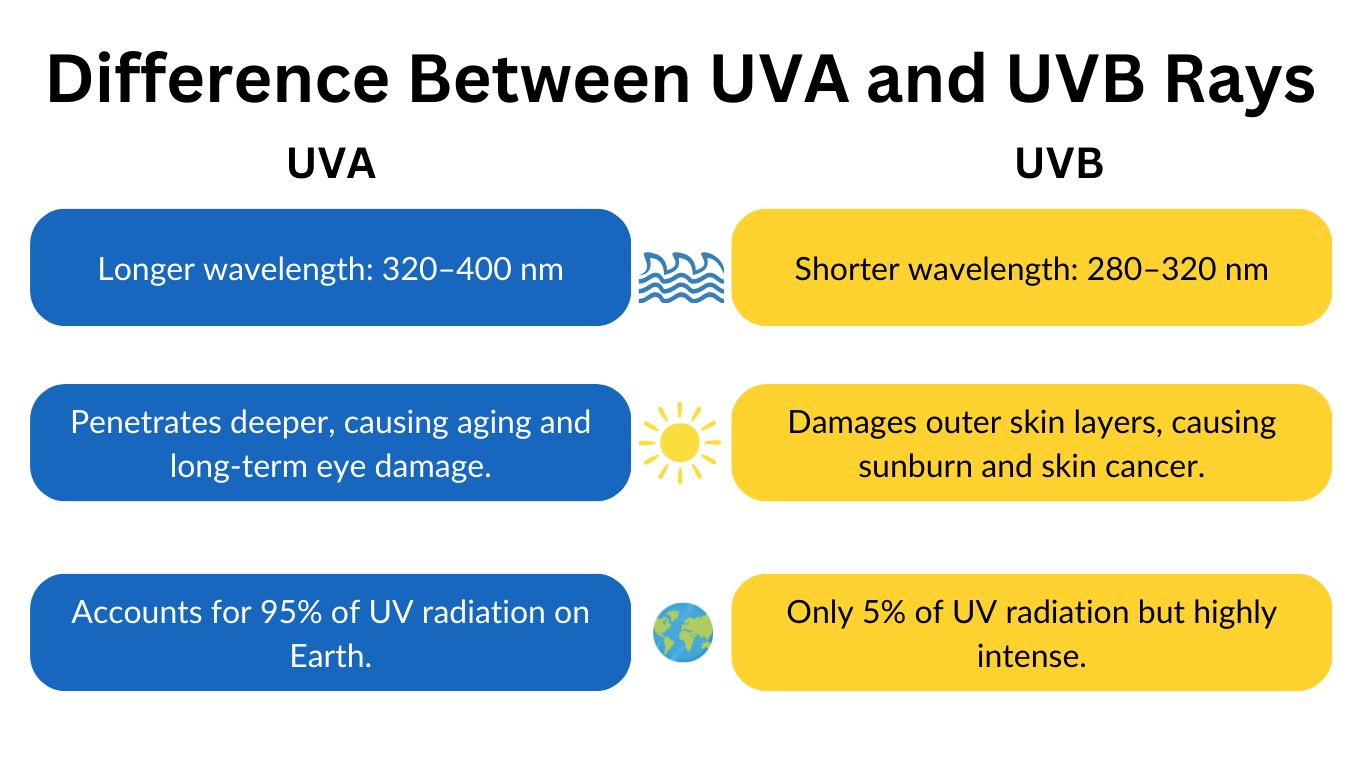
UVA
UVA has a longer wavelength (320-400nm). It penetrates deeper into the skin and eyes. Hence, it causes premature aging, wrinkles, and long-term eye damage. UVA damage builds up over time without showing any signs at first.
UVB
UVA has a shorter wavelength (280–320 nm). It affects the outer layers of the skin. UVB is the primary cause of sunburn and skin cancer. Unlike UVA’s gradual damage, UVB causes immediate effects.
Both UVA and UVB cause eye conditions like cataracts and other eye damage. This makes the use of UV protection glasses essential.
6 Signs Your Glasses Don’t Have UV Protection

Not all sunglasses are the same. Just because they give you a dash look and are dark to cut out all the light, does not mean they’re protecting your eyes. Here are key signs that your glasses might not be UV protection glasses:
1. No UV Protection Label
If your sunglasses don’t have a label that says “UV 400” or “100% UV protection,” then that’s your red flag. Genuine & high-quality sunglasses mention the tag of UV protection properly.
2. They Were Extremely Cheap
While price doesn’t always determine quality, extremely cheap sunglasses, especially from street vendors or online seller—often skip UV protection costs. Because as they say, “if it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.”
3. You Bought Them as a Fashion Accessory
Sunglasses are a fashion accessory that amps up your look. But for eye safety, always double-check them before assuming style includes safety.
4. Your Eyes Feel Strained in Sunlight
Wearing non-UV lens glasses worsens eye damage. Because when you buy dark tint, they make your pupils dilate, which in turn lets more UV rays enter your eye. If your eyes feel tired or sensitive despite wearing sunglasses, that’s a clear warning sign.
5. They’re Just Lightly Tinted
Lighter tints like yellow, pink can still offer UV protection only if they have UV-protecting lenses. If not, they might just be for a cosmetic effect.
6. No Brand or Trustworthy Manufacturer
Eyewear brands and trustworthy manufacturer specialize in protective lenses and will never skip UV protection in their sunglasses. If you can’t find any brand or manufacturer trace, you may be wearing just a style over quality.
Top Benefits of Wearing UV Protection Glasses Daily

The benefits of wearing UV protection glasses for your eyes are:
- Minimum to Zero Eye Strain: Cuts out excessive brightness, giving comfortable vision.
- Prevention of Eye Diseases: By shielding your eyes from harmful UV rays, these glasses reduce the risk of cataracts, macular degeneration, and other eye conditions caused by the sun.
- Younger Looking Eyes: Prevents premature aging, wrinkles, and dark circles caused by sun exposure.
How to Choose the Best UV Protection Glasses For Your Eyes?
Consider these factors when you choose to buy UV protection sunglasses:
- UV 400 Lenses: Look for sunglasses that have a label that mentions 100% UV protection or UV 400 or anti-UVA & UVB.
- Lens Quality and Type: If you drive a lot or love outdoor activities like sports, then you must get high-quality UV protection sunglasses with polarized lenses. For better protection and to block glare, polarized lenses work best.
- Wraparound Frames: If you are into cycling, running, walking, or intense sports, then get wraparound frames, which prevent UV rays from entering from the sides.
- Anti-Reflective Coating: You can also get mirrored sunglasses that block 100% of glare and give better comfort and clarity.
Conclusion
UV protection glasses are a must-have for better eye health and to give 100% protection to your eyes from the harsh sun.
Whether you are casually strolling or planning to go for a summer vacation, investing in high-quality sunglasses with proper protective lenses is a very effective way to shield your eyes and the thin skin around them.
Don’t wait for the sun to harm you; buy UV protection sunglasses now!
FAQs on UV Protection Glasses
1. Can regular goggles protect your eyes from UV rays?
Not necessarily. Check for UV 400 or 100% UV protection or UVA & UVB protection labels before making a purchase.
2. Are polarized sunglasses the same as UV protection glasses?
No. Polarization blocks glare but does not guarantee UV protection. You can get polarized sunglasses with UV protection to have both features.
3. Is it OK to wear UV protection glasses all the time?
In general, wearing UV protection sunglasses is safe. But wearing them all the time can affect your eye health, as eyes need natural light of varying intensity for proper functioning.
Share this content:




Post Comment